Hurumanu: The Water Cycle
AIM: TO LOOK AT THE WATER CYCLE AND HOW CLIMATE CHANGE IS AFFECTING IT.
Definition:
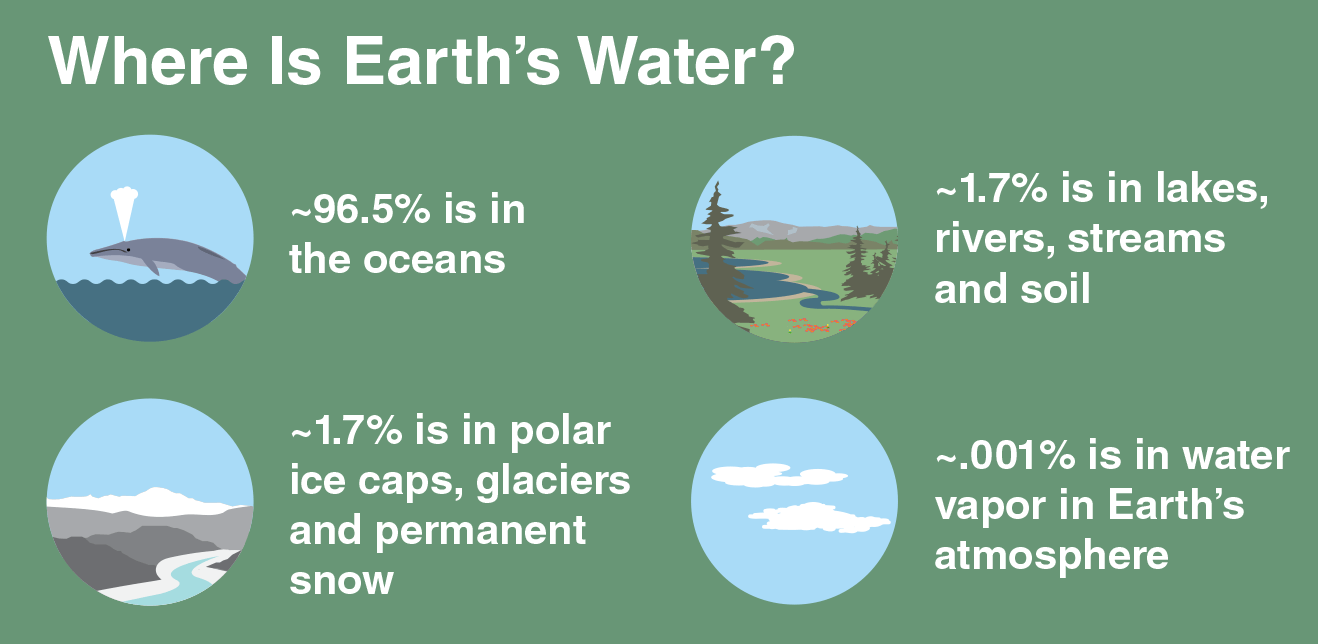
Scientific words:
- Evaporation. When water is heated by radiant energy it turns into water vapor.
- Transpiration. Evaporation from plants.
- Condensation. When water vapor cools, molecules join together and form clouds.
- Precipitation. When clouds get heavy the waters falls as rain, sleet, hail, or snow.
- Acidification: the action or process of making or becoming acidic.
We will be conducting an experiment that looks at the different ways that climate change is affecting the water cycle.
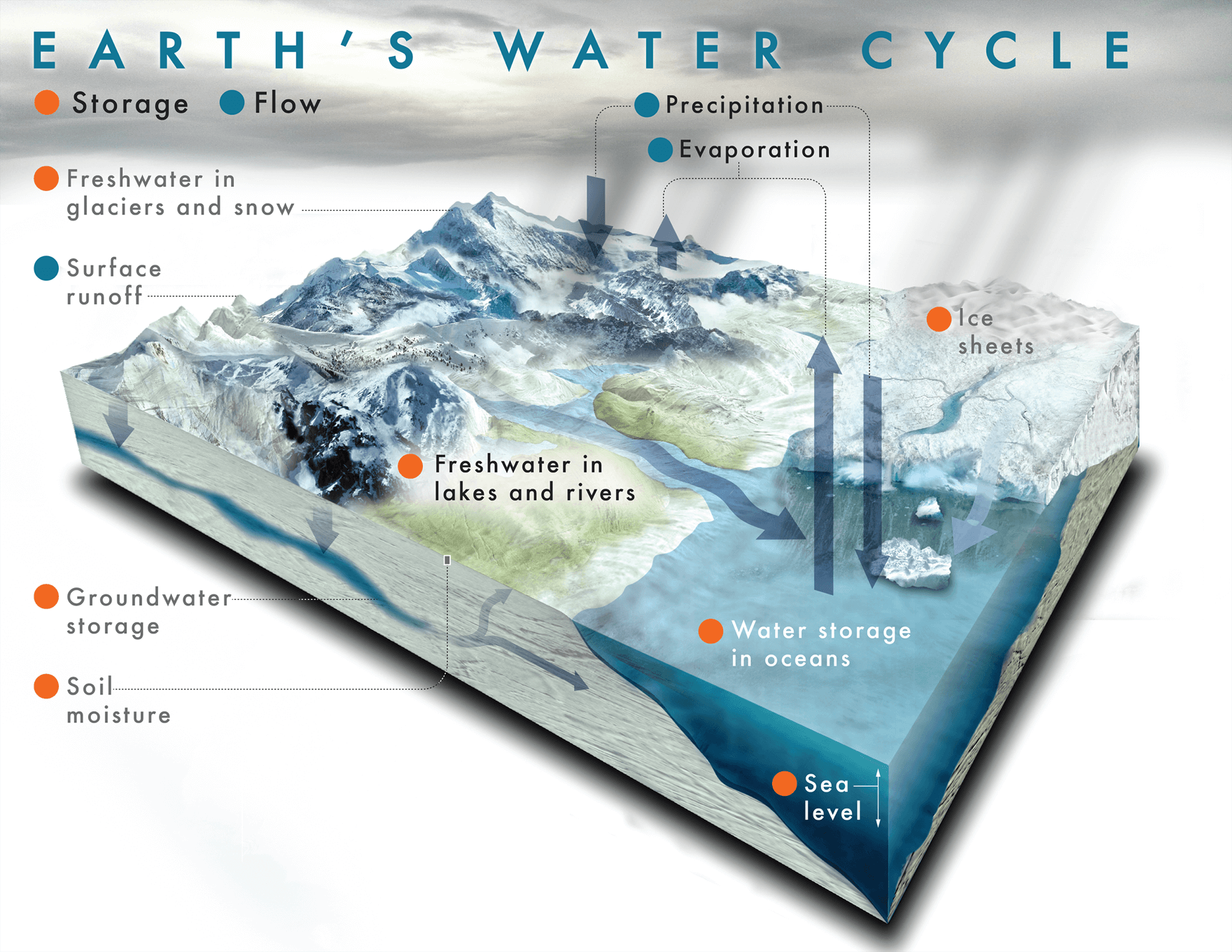

THE WATER CYCLE EXPERIMENT
Bag 1: Normal Water cycle
Bag 2: Water cycle with CO2 added: like Oceans in climate change
Bag 3: Water cycle with ice added: like Antarctica in climate change
Material:
Steps:
Two Images:
Findings:
The Water Cycle: Bag 1
|
CO2 Water Cycle: Bag 2
Acid
|
Desert Water Cycle
Bag 3
| |
Does it cycle?
| |||
Amount of Water
| |||
Acidity
|
Other comments:
Conclusion:
Draw a labeled diagram of the Water Cycle
Water cycle words:
- Precipitation, the action or process of precipitating a substance from a solution.
- Hurricanes, a storm with a violent wind, in particular, a tropical cyclone in the Caribbean.
- storms, a violent disturbance of the atmosphere with strong winds and usually rain, thunder, lightning, or snow.
- Evaporation the process of turning from a liquid into vapor
- Carbon Dioxide a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning carbon and organic compounds and by respiration. It is naturally present in the air (about 0.03 percent) and is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis.
- Water a colorless, transparent, odorless liquid that forms the seas, lakes, rivers, and rain and is the basis of the fluids of living organisms.
- Oceans a very large expanse of sea, in particular, each of the main areas into which the sea is divided geographically.
- Water vapor, water vapor or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Unlike other forms of water, water vapor is invisible.
- The freshwater of or found in fresh water; not of the sea.
- Flooding is when the water is flooding everywhere like the flood/water can break houses and all kinds of things.
SOLO Hexagons Activity
Water cycle words:
Water cycle words:
- Precipitation
- Hurricanes
- Storms
- Evaporation
- Carbon Dioxide
- Water
- Oceans
- Water vapor
- Freshwater
- Flooding

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.