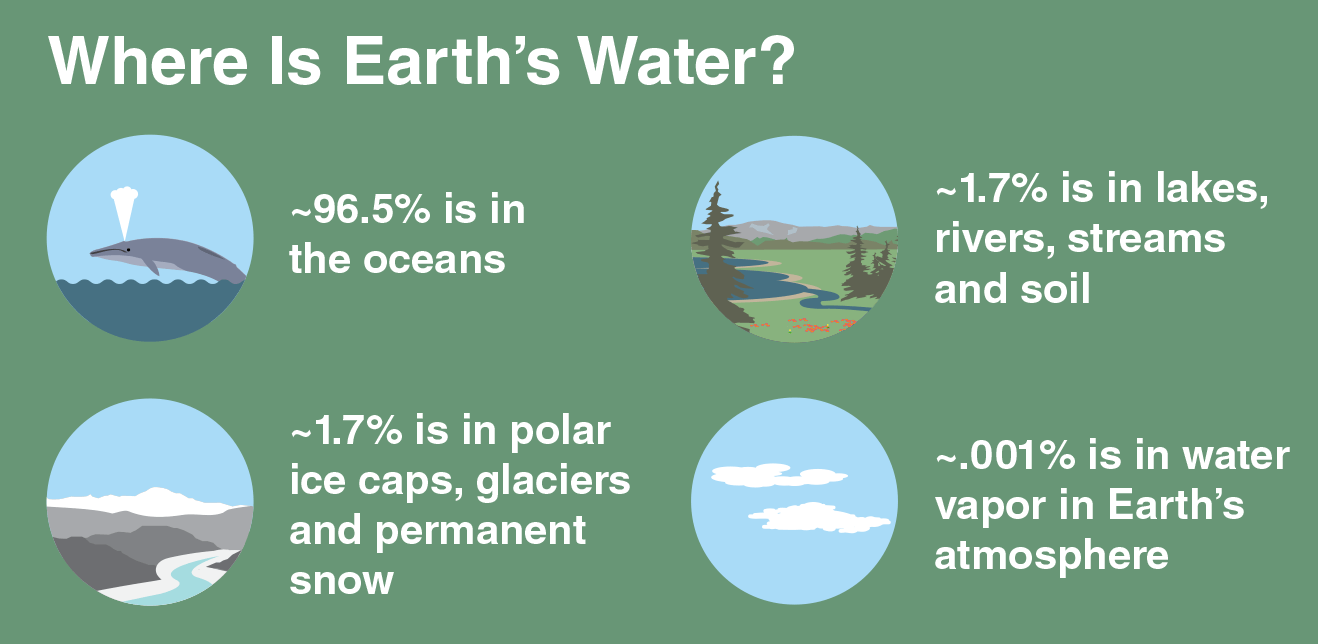
Plastics:
Cycling or walking: you won't have to use your car And bye fuel for your car.
Paper: You don't have to cut more and more trees down.
Steel: You will have to go and use coal if we burn all o the steel we have at the moment
Video questions:
What is Zero Waste?
one of the quickest and cheapest ways a community can immediately reduce climate impact
What can we do on the planet?
- Redesign
- Recycle
- Reduce
- Reuse
What do we need to recycle?
- Plastic-Bottles, Straws,
- Paper
- Cardboard-Box's
What does recycling do?
cuts down more plastic that is on the land, and if we don't recycle things it can kill our animals in the sea
How much of our rubbish is food scraps?
What does soil due to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
What do we need to do?
- Make People stop littering.
- Have Zero tolerance for lettering.
What is a carbon footprint?
How can you make your Carbon Footprint smaller?
ENERGY SAVING TIPS FILM
Name 4 of the tips.
- Turn off your lights in your room if you ain't there
- Turn off all the switches that you plug in your electricity
AT WHAT RATES DO DIFFERENT ITEMS DECOMPOSE?
MY INVESTIGATION.

Choose 5 items from the list and investigate them.
Aluminum can:
plastic:
milk carton:
plastic glass:
plastic glass:
You need to answer three questions.
Name: Latisha
- How long do they take to decompose?
Aluminum can:200-500 years
glass bottle: One million years.
plastic:3-4 weeks
milk carton: Five years
plastic glass: 450 years
1. What resource/fossil fuel are they made from?
plastic glass: 450 years
1. What resource/fossil fuel are they made from?
- How is this resource recycled?
- How does this object contribute to climate change?